Arc Welding VS Spot Welding, What’s The Difference
In the welding industry, there are many types of welding. Arc welding and spot welding are among the most common techniques. They are often used in different fields and play important roles in various industries. As a beginner, it might be hard to understand the differences. If you want to learn about the distinctions between arc welding and spot welding, the following article will explain them in detail.
What Is Arc Welding?
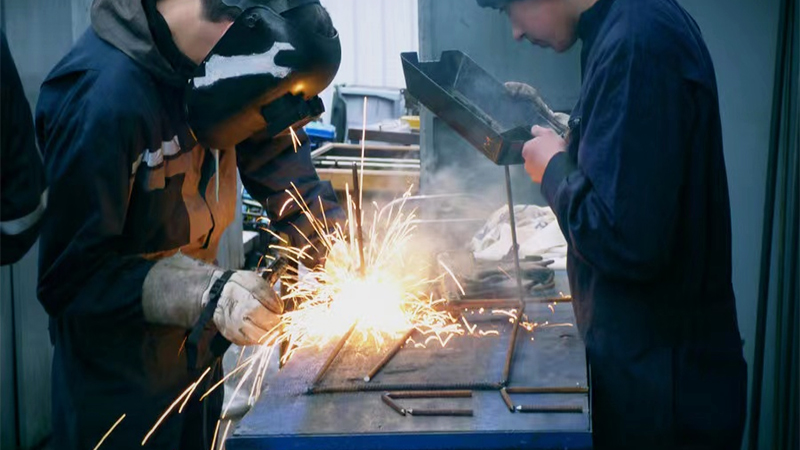
Arc welding is a process that uses the heat generated by an electric arc to melt and join metals together. The power source for arc welding can provide either direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC). Depending on the welding requirements, arc welding can use either consumable or non-consumable electrodes. Developed in the late 19th century, arc welding played a significant role in shipbuilding and is also widely used in the automotive and heavy industries.
What Is Spot Welding?
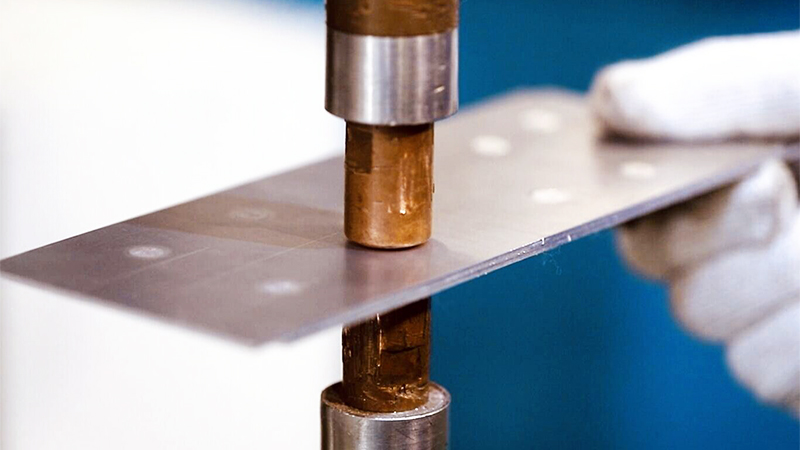
Spot welding is a form of resistance welding that uses electric current to generate heat and apply pressure, causing the contact points between the workpieces to form a weld nugget or plastic state and join together. It is a traditional welding method that primarily uses copper electrodes to conduct electricity. The electric current passes through the workpieces, melting them at the contact points, and when the current stops, the pressure continues to hold the contact points together, forming a joint.
Difference Between Arc Welding And Spot Welding
Principle of Welding
Arc welding and spot welding operate on different principles. Arc welding uses an electrode and the workpiece to create an electric arc, generating heat. The high temperature melts the electrode into a liquid that fills the metal joint and cools to form a weld, joining the two metal parts. This is a form of liquid-state welding.
Spot welding, on the other hand, involves stacking two workpieces and applying pressure with two electrodes. Electric current heats the contact points between the electrodes and the workpieces, causing them to melt. Upon cooling, the parts are joined together, making it a solid-state connection.
Requirement of Filler Material
In the welding process, arc welding can use filler metal or not. When welding two workpieces together, filler material might not be needed. Spot welding does not require filler material; it directly heats the workpieces to a plastic state to join them.
Application scope
Spot welding and arc welding have different applications. Arc welding is suitable for welding complex shapes and large metal workpieces, making it ideal for repairing and maintaining large parts and heavy industry applications. Spot welding is generally used for small parts about 3 millimeters thick and is better for high-volume welding. It is commonly used in the automotive and home appliance industries.
Welding Time
Arc welding metal takes a longer time and is not a one-time process. Spot welding is much quicker and can complete a product in a minute or even a few seconds.
Welding Cost
Arc welding has a relatively low welding cost, but because of its technical difficulty, the labor cost for skilled arc welders is high. Spot welding has a higher overall cost, with one spot welding machine costing as much as several arc welding machines. However, the labor cost for operators is low, which can save costs in the long run.
Requirement of External Pressure
For external pressure requirements, arc welding generally does not need external pressure. The arc generated by the power source melts the workpiece and filler material. Spot welding, however, requires air pressure to press the two workpieces together, and then heat is generated through the current.
Operational safety
Arc welding is technically challenging and requires skilled welders. If you want to use arc welding, you must undergo professional training. Spot welding is simpler and safer, requiring relatively less skill. Operators only need basic training to get started.
Conclusion:
The above are the main differences between arc welding and spot welding. When choosing a welding method, you should consider these points. Whether to choose spot welding or arc welding mainly depends on the product you need to weld, its material, and characteristics. For example, if you want to weld a large stainless steel pipe, it’s best to choose arc welding because spot welding is only suitable for small parts. So before choosing a welding method, be sure to analyze each situation from multiple perspectives.