How To Spot Weld, Benefits In The Automotive Industry
Metal sheet welding is a crucial part of the production process for various metal products. Spot welding is widely used in the automotive manufacturing industry, home appliance hardware industry, and sheet metal box industry. Modern technology demands increasingly higher welding quality. In this article, we will explain the spot welding process in detail and discuss the advantages of spot welding in the automotive industry.
What Is Spot Welding
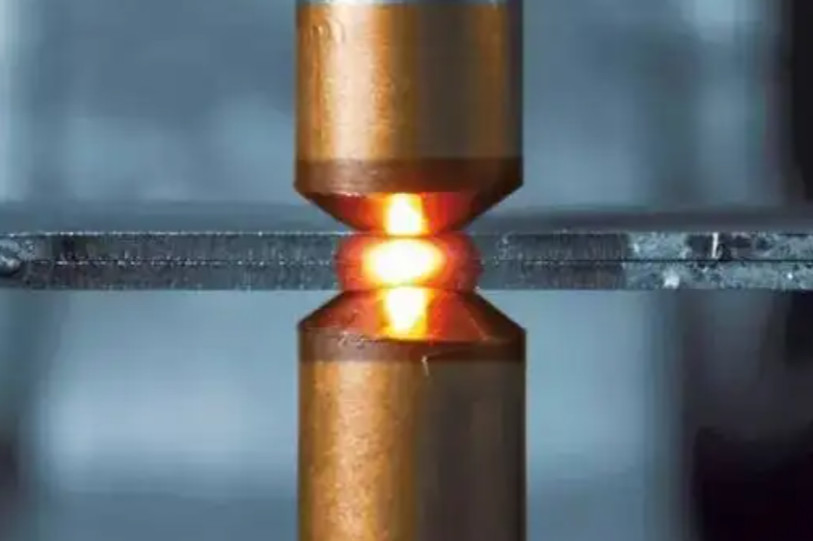
Spot welding is a type of resistance welding. It involves placing two workpieces between upper and lower electrodes, heating them with an electrical current, and applying pressure to create a plastic state at the contact surface of the workpieces, allowing them to bond together. Its principle is simple: by conducting electricity through two copper electrodes, the resistance increases the temperature of the workpieces, causing them to melt and bond together. That’s why it’s also called resistance welding. Compared to other welding processes, spot welding doesn’t require adding welding material, and the operation is simple.
How To Spot Weld ?
1: Workpiece Surface Cleaning
Spot Welding Commonly Materials
Aluminum: Aluminum is very common in spot welding, especially in the automotive industry, where its lightweight characteristics can replace rigid structures. However, welding aluminum is more challenging because of its high conductivity, requiring about twice the current of ordinary materials. Therefore, when welding aluminum, you must choose equipment with higher power.
Steel: Steel is the most common material in spot welding. It is a hard material, and many automotive components use steel. Spot welding is generally used for welding car bodies and rigid nut components.
Copper: Spot welding copper requires special techniques. Copper has high thermal and electrical conductivity, making it prone to sticking to electrodes. Therefore, we choose tungsten or molybdenum electrodes. During welding, brazing material needs to be added between the two workpieces, so copper brazing is commonly used.
Galvanized steel: Welding galvanized steel is more difficult than welding steel, requiring higher current. The melting point of the galvanized coating is lower than that of steel, so it is easy to overflow and form splashes during welding.
Workpiece Surface Cleaning
Before welding, it’s important to check if the workpieces have rust or oxidation. If they do, the workpieces need to be treated. You can use sandpaper or a grinder to make the surface smooth. Otherwise, there will be a lot of splatter, which can affect the welding quality.
2: To Consider 4 Variables Before Welding And Setting Parameters
Pressure
Choosing the appropriate pressure is crucial. If the electrode pressure is too high or too low, it can weaken the weld’s strength and increase its dispersion. When welding, it’s important to consider the characteristics of the workpiece when setting the pressure.
Welding Time
Setting the appropriate welding time is crucial. If the welding time is too short, the workpiece may not melt sufficiently to meet the welding requirements. On the other hand, if the welding time is too long, the workpiece is prone to deformation, resulting in larger weld marks.
Welding Current
The welding current and time complement each other, but they also have their limits. Finding the right balance between the two is key to producing perfect welds.
3: Spot Welding Machine
The equipment required for spot welding is a spot welding machine, which comes in different models. Choosing the right spot welding machine depends on the characteristics of the workpiece and the welding requirements. For example, if you want to weld together two 2mm stainless steel plates to achieve the required parent material strength, you’ll need to choose a spot welding machine with higher power. A standard spot welding machine with 130KVA can accomplish this. However, if you need to weld 2mm thick aluminum plates, you’ll need a standard spot welding machine with 260KVA.
4: Place The Workpiece Between Electrodes And Start Welding
Once you’ve selected a suitable spot welding machine, it’s time to start welding. After connecting the power supply and adjusting the parameters, place the prepared workpiece between the two electrode cap. Press the foot pedal button, and the electrodes will press down, heating and compressing the workpieces, thereby connecting the contact points of the two workpieces together.
5: The Peel Test After Welding
After welding the workpiece, it’s difficult to assess the strength of the weld with the naked eye alone. That’s when you need to use tools to test the weld’s strength. Peel testing is a great method. During peel testing, observe the maximum tensile force reached when peeling the workpiece. Some workpieces have specific requirements for this value to deem the weld acceptable.
The Benefits Of Spot Welding For Automotive Industry
Solid And Long-lasting Joints
Parts welded using resistance welding create strong and durable joints. Products made this way are sturdy and stable, which is crucial in the automotive industry. For instance, if a nut isn’t securely welded, it could lead to accidents on the road. Precision and reliability are paramount in the automotive sector, where even the slightest error is unacceptable. Therefore, resistance welding plays a crucial role in ensuring these standards are met.
Uniformity In Joints
In welding automotive components, it’s not only important for the welds to be strong but also for the welded products to look aesthetically pleasing. Resistance welding can achieve this requirement. Especially for welding the car body, every weld point should be inconspicuous, as it affects subsequent processing and the overall appearance of the vehicle.
Joining Of Dissimilar Materials
Resistance welding is also suitable for welding dissimilar materials. In the automotive industry, there are components where different metals need to be joined together. This is where resistance welding comes in handy, as it can join dissimilar materials, such as steel and aluminum.
Welding Speed
Resistance welding does not require filler wire. It’s faster for welding small parts. In the automotive industry, where mostly small components are welded, the process is quick and easily automated, saving labor and boosting welding efficiency.
Repeatability
Due to its suitability for welding repetitive products, resistance welding may require parameter and equipment adjustments when switching to different specifications. Hence, it’s more suitable for welding high-volume products. Automotive components, precisely because of this characteristic, find resistance welding particularly suitable for the automotive industry.
Resistance welding is increasingly widely used in today’s industrial sectors. Its technology is continuously updated to adapt to industrial development, moving towards automation. To learn more about resistance welding, please follow our updates.
FAQ:
1、What welding method should I use to weld a stainless steel oil drum that needs to be tightly sealed?
For airtight requirements, you can use the seam welding, a seam welder can do it.
2、What kind of welding machine is generally used for car body parts?
Car bodies typically use spot welding gun, which are flexible and easy to automate.
3、What power spot welder is needed to weld 2mm thick stainless steel?
A 130kVA spot welding machine will work well.
4、How do I weld an M8 nut to a 2mm carbon steel plate?
You can use a projection welding machine.
5、How do I adjust spot welding parameters?
Adjust the parameters based on the specifications of your workpiece and the welding requirements.
6、How to spot weld without a welder?
You can use a robot for automated loading and welding.
7、How to weld aluminum?
Aluminum has a low melting point, so you need higher power. A MFDC spot welder can be used.